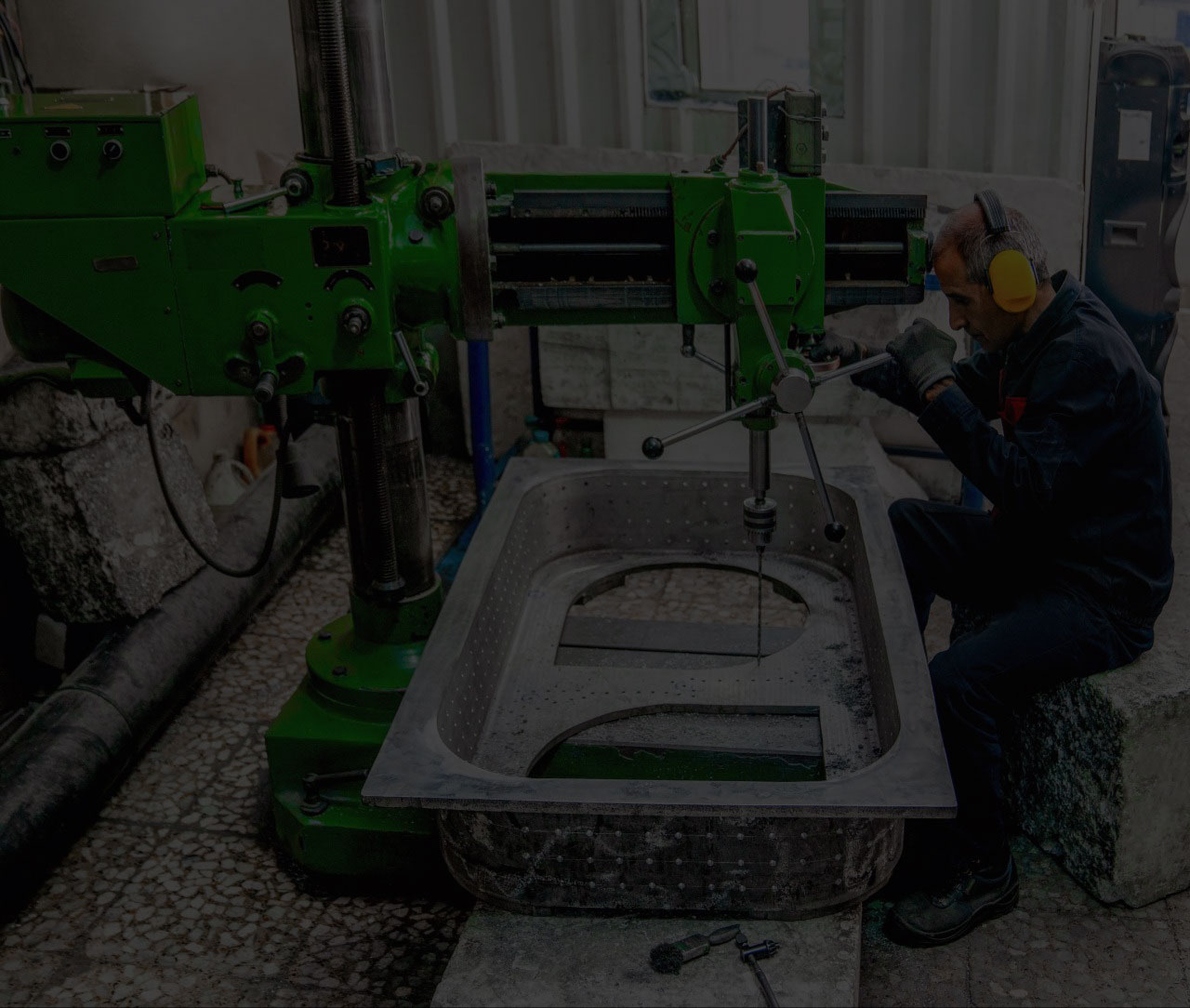


EPS Molding at Iranian West Foam Manufacturing Company
The wisest way to protect what you pack
Iranian West Foam Manufacturing Company operates an on-site EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) molding unit designed to increase production speed, simplify operations, and ensure consistent product quality.
Packaging plays a critical role in protecting manufactured goods. Proper packaging safeguards products during storage, transportation, and final delivery to the customer.
EPS packaging functions as an effective shock absorber and must be designed according to the specific shape and dimensions of each product. Therefore, creating protective EPS foam requires a custom mold tailored to every individual item.
For all types of EPS packaging solutions, our team of experts is ready to assist you.
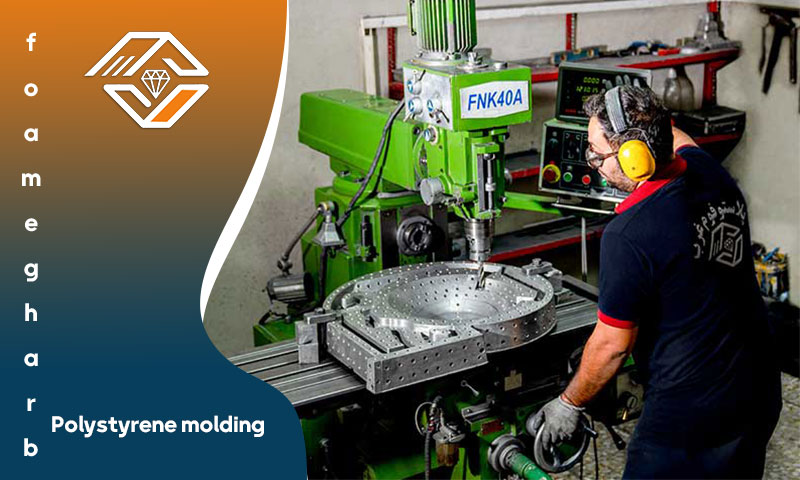

EPS (Expanded Polystyrene) Molding
Mold making is a fundamental step in all industries. EPS molds are used to shape polystyrene components and are typically designed as two-part, openable molds. Most EPS molds are made from aluminum.
The alloy used in mold production has a direct impact on both the quality of the final EPS product and the longevity of the mold itself. Since EPS molds are exposed to steam, hot water, and thermal fluctuations on a daily basis, selecting the right alloy is crucial. Additionally, the quality of all materials used in every part of the mold significantly affects its performance.
How to Order a Custom EPS Mold
To order a custom-designed EPS mold for your product, please provide our experts with the following:
Your product or the desired packaging foam design
The external dimensions of the product
The required monthly or annual production volume
Our engineering team will evaluate all design details, calculate the required time and cost, and contact you to finalize the mold manufacturing agreement.
To guarantee 100% accuracy, an initial prototype mold is created and tested on the product. Once the design is approved, full-scale mold production begins, and the final prototype is delivered.
EPS Mold Manufacturing Process
The process of producing an EPS mold includes the following steps:
- Creating the initial model from wood or EPS
- Sending the model to the foundry for aluminum casting
- After casting, the aluminum components are transferred to our in-house mold manufacturing unit for milling, turning, CNC machining, and finishing
- Assembling the mold and preparing it for EPS production according to customer specifications.

Product Design and Pre-Production Approval
To manufacture a mold for any EPS packaging, a 2D or 3D blueprint—or a physical sample of the product—is required. Our experts evaluate the design, prepare a suitable prototype, and send it to the customer for review. Once final approval is received, the mold manufacturing process begins.
Packaging EPS Mold Manufacturing
Packaging foam is one of the most widely used and essential forms of EPS, providing reliable protection for a variety of products. As a result, manufacturing high-quality molds for packaging EPS is of great importance.
Key Considerations for Packaging EPS Mold Production
Molds must be built from durable, high-quality materials
The mold surface must be precisely machined and finished to achieve a smooth and uniform EPS surface
Molds should always be kept clean and dry during operation
All mold connections must be properly installed and adjusted to prevent opening or steam leakage
Proper maintenance significantly extends mold lifespan
CAD software can be used to design accurate and efficient molds
Continuous quality control—through mechanical and thermal testing—is essential to ensure product quality
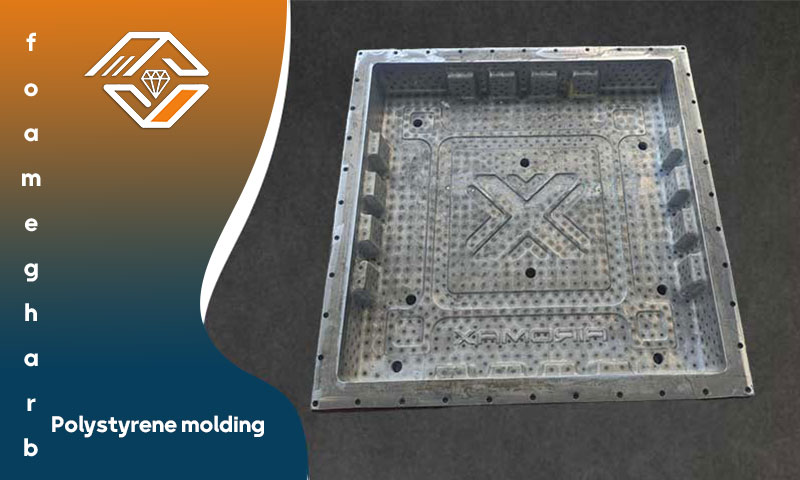
Aluminum Molds for EPS Production
EPS molds are commonly manufactured from either cast aluminum billets or rolled aluminum blocks. Rolled aluminum offers greater durability but comes at a higher cost.
Most molds used in EPS production are made from cast aluminum alloys. Selecting the right alloy is essential, as it must provide both corrosion resistance and good machinability. Choosing a reputable mold manufacturer ensures that the material quality meets required standards.
Since mold manufacturing represents a significant investment in the EPS production line, premium materials and advanced technologies should be used. Lower prices may compromise quality and increase long-term costs.
Applications of Aluminum Molds in EPS Production
Construction EPS Blocks
Aluminum molds are used to produce EPS blocks applied in thermal and sound-insulating walls, lightweight ceilings, and earthquake-resistant structures.
Packaging Components
EPS is widely used to manufacture protective packaging for electronics, household appliances, and fragile items. Aluminum molds enable precise, complex shapes in high quality.
Industrial EPS Parts
In various industries, EPS is used to produce functional components such as pipe insulation, engineered parts, and specialty items. Aluminum molds support fast, high-precision production.
Decorative Products
EPS is also used for decorative shapes such as ornamental columns, frames, and lightweight architectural elements. Aluminum molds allow fine surface detailing for these products
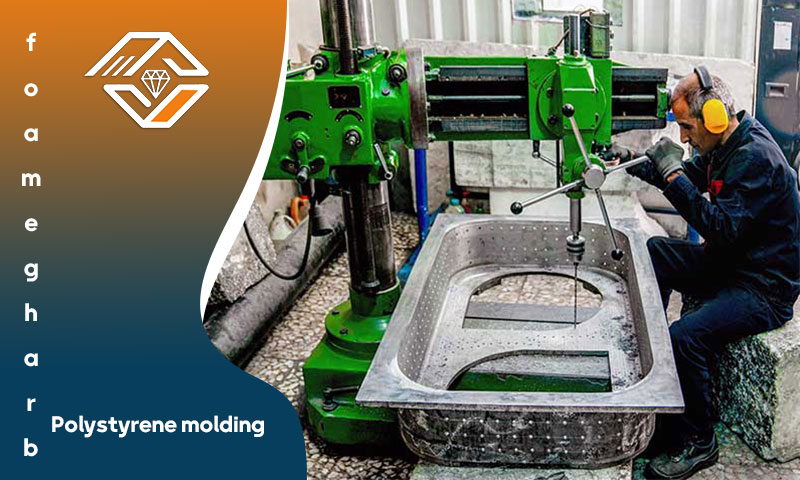

Advantages of Aluminum Molds in EPS Production
High Precision: Aluminum’s excellent machinability enables molds with fine detail and accuracy, essential for complex EPS components.
Superior Thermal Conductivity: Ensures even heating and cooling, resulting in consistent product density and appearance.
Durability and Long Lifespan: Aluminum resists rust and corrosion, making it cost-effective for long-term, high-volume production.
Lightweight Structure: Easier handling and installation during mold setup and production.
Design Flexibility: Aluminum molds can be manufactured in a wide variety of shapes and sizes to accommodate diverse EPS applications.
Role in Improving EPS Product Quality
Smooth aluminum mold surfaces prevent defects such as voids or marks. Their fast heating and cooling capabilities also increase production efficiency and reduce operational costs
EPS Mold Coating (PTFE/Teflon Coating)
During EPS production, molds are exposed to styrene, pressurized steam, and repeated thermal cycles. This can lead to corrosion, wear, and material adhesion over time. Applying a PTFE (Teflon) coating is a proven solution widely used in the industry.
Benefits of Teflon Coating
Minimizes material adhesion and allows easier part release
Extends mold lifespan with strong corrosion and oxidation resistance
Reduces production downtime and increases cycle speed
Prevents defects such as voids, scratches, and surface marks
Reduces reliance on release agents and lowers maintenance costs
Provides excellent resistance to heat and steam
Improves uniformity, density, and overall surface quality of EPS components
Applications of EPS Molds
EPS molds are widely used across multiple industries, especially for packaging and transportation. Common applications include:
Electronic Product Packaging
Used to protect electronics during transportation and storage, preventing damage from shock, vibration, and temperature fluctuations.
Food Packaging
Ideal for transporting sensitive foods such as protein products, fruits, and vegetables, where insulation and impact protection are essential.
Chemical Product Transportation
Used to package and protect items like paints, resins, and adhesives, providing cushioning against external impacts
Construction Mold Making
EPS molds serve as lightweight, reusable alternatives to traditional concrete or wooden molds. They can be custom-designed to create architectural and structural elements such as bridge components or coastal barriers.
Advantages of Using Proper EPS Molds
Using well-designed, high-quality molds in EPS production offers several important benefits:
Improved Product Quality: Precision molds ensure consistent density and stronger, defect-free EPS components.
Reduced Material Waste: Accurate mold design minimizes production waste and lowers overall manufacturing costs.
Increased Production Speed: Optimized molds allow faster production cycles and higher output efficiency
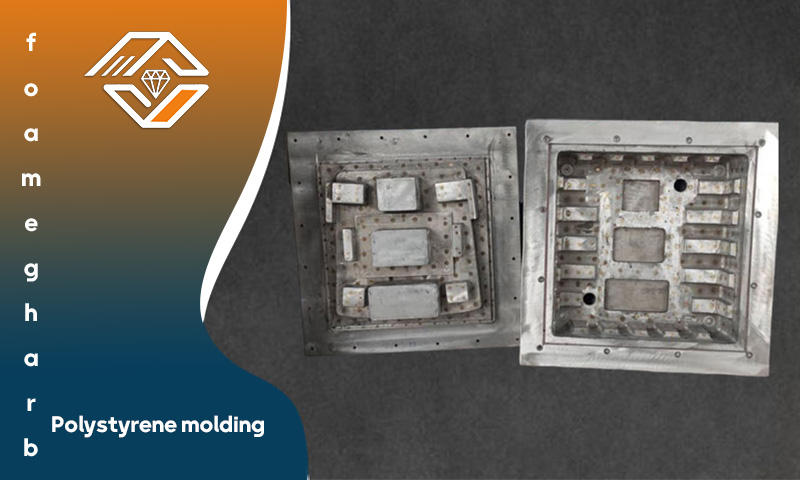
Methods for Reinforcing EPS Molds
Since most EPS molds are made from cast aluminum alloys, the chosen material must offer both corrosion resistance and sufficient hardness for machining. Using low-quality or recycled aluminum may reduce mold quality and shorten its lifespan. Given the critical role of molds in EPS production, reinforcement methods can significantly improve performance and durability.
Key Methods for Reinforcing EPS Molds:
- Comprehensive Design Review:
The mold design must be thoroughly analyzed to ensure correct geometry, dimensions, and material distribution. - Use of Metal Straps or Structural Supports:
Metal braces help prevent deformation under high pressure. - Reinforced Cement Structures (When Applicable):
In certain designs, adding reinforced cement elements increases structural stability. - Use of Professional-Grade Equipment:
High-precision machinery (milling, CNC, etc.) ensures correct dimensions and cleaner finishes. - Skilled Workforce Training:
Workers must be trained in proper mold manufacturing and maintenance techniques. - Regular Testing and Sampling:
Ongoing sampling ensures that mold performance remains consistent and defects are detected early. - Use of High-Quality Raw Materials:
Fresh, certified materials directly affect mold durability and production quality. - Continuous Quality Control Procedures:
Implementation of strict QC standards throughout production improves reliability and extends mold lifespan.
Conclusion
EPS mold manufacturing is a highly precise and detailed process that requires the right materials, expert design, and strict quality control. By choosing proper alloys, ensuring accurate engineering, and investing in advanced technologies, manufacturers can produce high-quality EPS components with superior strength and performance.
Given the critical role molds play in EPS production, prioritizing quality at every stage has a significant impact on overall efficiency, product reliability, and long-term success.
Main Products
Polystyrene packaging
Polystyrene Industrial
polystyrene construction
polystyrene cooler
